AI is referred to as the use of computers for reasoning, recognizing patterns, learning, or understanding certain behaviors from experience, acquiring and retaining knowledge, and developing various forms of inference to solve problems in decision-making situations where optimal or exact solutions are either too expensive or difficult to produce. AI creates a simulated experience that plays a vital role in the decision-making process. The use of machine learning techniques and case-based reasoning to reference previous knowledge of similar situations could save time, money, and workforce.
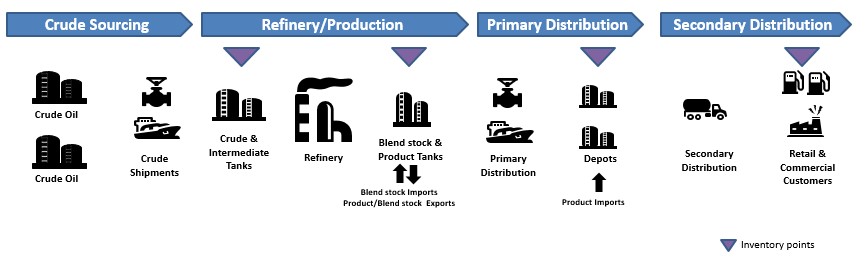
The oil and gas industry is one such place where millions of operations generate a huge quantum of data, which is impossible to be manually scrutinized, analyzed, and draw some trends from it. The supply chain for the oil and gas industry is a complex operation where there are several key decision nodes like crude purchase, price of the purchase, transportation to the refinery, refining operations, gantry operations, and retail sale of end products. As crude moves ahead in a stepwise manner, so does the complexity of decisions increases.
AI Enabling the Supply Chain Management in Oil and Gas Industry
There are several avenues that oil and gas companies are exploring in terms of the application of artificial intelligence in the supply chain of oil and gas operations. These areas are:
- Prediction of the market price of crude oil and finished products: This helps in taking decision for pricing contracts
- Optimization of the crude basket, warehouse, and logistics, inventories, shipping operations: This helps in making sure that the optimal kind of crude oil is selected and it is being delivered and handled appropriately
- Risk hedging: Appropriate investments to offset the risks due to change in supply, demand, and prices
- Vessel tracking: Tracking the deliveries to handle warehouses and demand from end customers
- Planning and scheduling: Planning and scheduling allows the company to better utilize their assets, time and inventories to fulfill the orders with a minimal time lag
- Deploying Robotic Process Automation: Operations which are repetitive and high on consuming human to be replaced by robots leading to drastic impact in terms of productivity, efficiency, and accuracy on the business processes industry
- Predictive capabilities are helping demand forecasting: When inventory lags demand, companies suffer losses. AI is ramping up efficiencies in network planning and predictive demand, allowing merchandisers to become more proactive. By knowing what to expect, they can adjust the number of vehicles and direct them to locations where maximum demand is expected. This leads to lower operational costs.
- Chatbots are redefining customer support: 80 percent of all customer engagements can be handled by bots. AI can personalize the relationship between customers and logistics providers.
- Smart warehouses are more efficient: A smart warehouse is a fully automated facility wherein most work is done through automation or software. Deliveries can be scheduled through logics without missing any deadlines.
- Algorithms are improving delivery times and reducing costs: In the logistics business, every mile and minute matters. Companies can use a route planner based on genetic algorithms to map out optimal routes for deliveries.
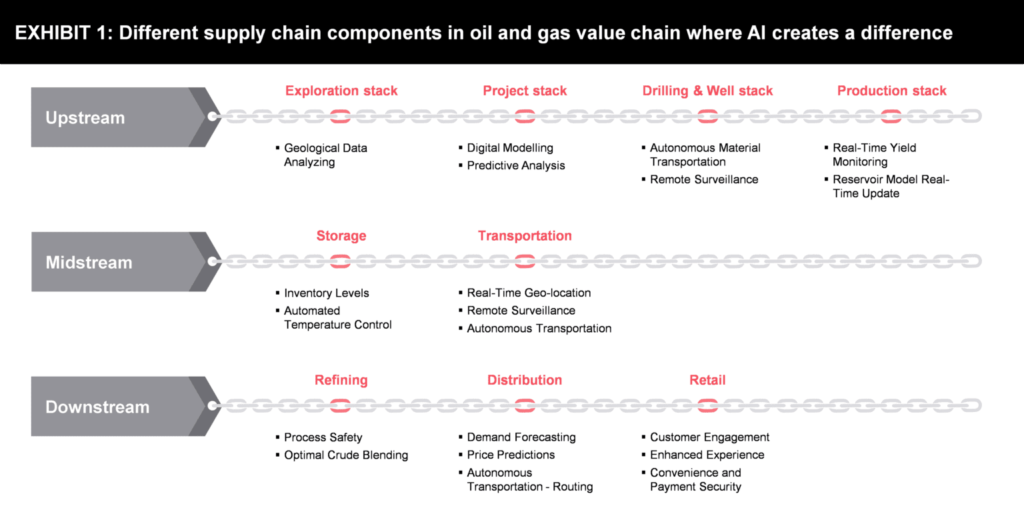
AI supports distinct functions across the oil and gas value chain, each of which has an element of the supply chain involved.
- Upstream: In the upstream business, the supply chain is important from equipment and material transportation aspects. Slight delay or unavailability of spares/ key components can lead to huge operational losses. AI can coordinate the operations team with the warehouse making sure the availability of crucial parts.
- Midstream: In midstream business, it is more from storage and transportation of oil and gas through multiple mediums like ships, trucks, or rail. AI assists here in proper planning and execution, optimal route selection, etc.
- Downstream: In downstream business, AI helps refiners to plan optimal blending, forecasting the demand, estimating prices, and improvising customer relationships.
